Dosage
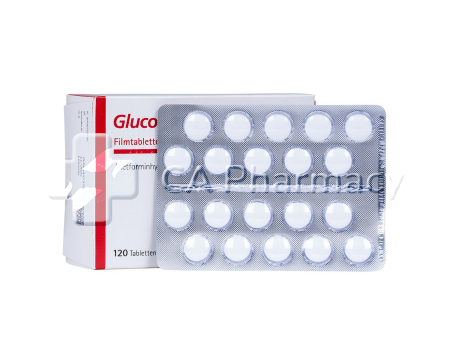
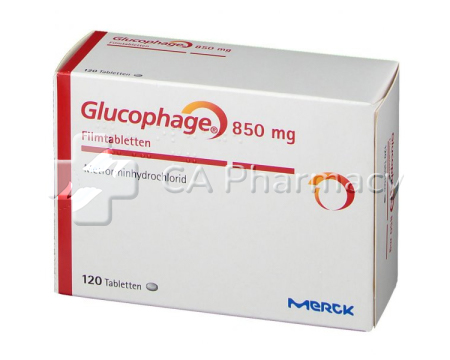
The dosage of Glucophage Metformin varies depending on the individual's needs and response to treatment. Typically, the starting dose for adults is 500mg twice a day or 850mg once a day. The dosage may be gradually increased to a maximum of 2,550mg per day, divided into three doses. It is crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Side Effects
Like any medication, Glucophage Metformin may cause side effects. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach upset, and a metallic taste in the mouth. These side effects are usually mild and subside with time. However, if they persist or worsen, it is essential to inform your healthcare provider.
Benefits
- Glucophage Metformin is a medication used to treat diabetes mellitus.
- It works by decreasing the amount of glucose produced by the liver and improving the body's response to insulin.
- Glucophage Metformin is commonly prescribed alongside insulin to help control blood sugar levels.
- The dosage of Glucophage Metformin varies depending on the individual and their blood glucose levels.
- Common side effects of Glucophage Metformin include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach upset.
- It is important to monitor blood sugar levels regularly while taking Glucophage Metformin to ensure proper glycemic control.
- Glucophage Metformin should not be used by individuals with severe kidney or liver problems.
- The extended-release formulation of Glucophage Metformin, called Glucophage XR, is also available.
- Glucophage Metformin should not be taken with certain medications, as it may cause harmful drug interactions.
- It is important to follow the prescribing doctor's instructions and warnings when taking Glucophage Metformin.
Glucophage Metformin is an effective medication for managing diabetes mellitus by reducing glucose production in the liver and enhancing the body's insulin response. It is often used alongside insulin to maintain better blood sugar control, with dosages tailored to individual needs.
While generally well-tolerated, common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach upset. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential to ensure effective glycemic control.
For added convenience, an extended-release version, Glucophage XR, is available. However, it is not suitable for individuals with severe kidney or liver conditions or those taking medications that may interact adversely.
Always follow the prescribing doctor's instructions to maximize the benefits and ensure safe use of Glucophage Metformin.
What are the possible interactions of glucophage metformin with other drugs?
Here are some of the possible interactions of Glucophage with other drugs:
- Insulin: Glucophage can be used in combination with insulin to help improve glycemic control. However, the dosage of insulin may need to be adjusted when starting or stopping Glucophage to avoid the risk of hypoglycemia or high blood sugar levels.
- Other diabetes medications: Glucophage may interact with other oral antidiabetic drugs, such as sulfonylureas or meglitinides, which can increase the risk of hypoglycemia. Your healthcare provider may need to adjust the dosages of these medications to ensure optimal blood sugar control.
- Medications that affect the kidneys: Glucophage is primarily eliminated through the kidneys, so drugs that affect kidney function can potentially interact with Glucophage. Certain medications, such as diuretics or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can increase the risk of lactic acidosis when used with Glucophage. Close monitoring of kidney function is essential in these cases.
Always consult your healthcare provider to manage these interactions effectively and ensure the safe use of Glucophage Metformin.
Is glucophage metformin safe for long-term use?
One of the main concerns with long-term use of Glucophage is the potential for developing vitamin B12 deficiency. Studies have shown that prolonged use of Glucophage can lead to reduced levels of vitamin B12 in the body. Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, numbness or tingling in the hands and feet, and problems with memory and concentration. Regular monitoring of vitamin B12 levels and supplementation if necessary can help mitigate this risk.
Another potential side effect of Glucophage is gastrointestinal issues. Some individuals may experience symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or abdominal discomfort when starting Glucophage. These side effects are usually temporary and improve over time. However, if they persist or worsen, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional.
Rarely, Glucophage can cause a serious condition called lactic acidosis. This is a buildup of lactic
How long does it take to see the effects ?